It is important to know when designing what types of fabrics are to be used in a collection. For example, if you want a specific drape; the weight of the fabric will matter and whether it’s mixed with polyester, wool or cotton. It could also be a performance fabric such as the ballistic nylon used in the Vexed Parka which is used for protection.
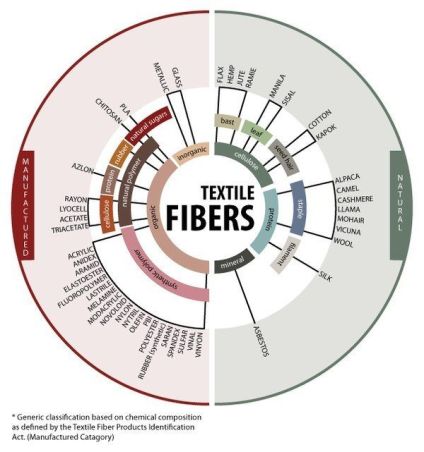
Types of fibres:
Textile materials are made in three stages:
- SPINNING fibres are spun into yarns
- WEAVING/KNITTING: yarns become fabrics
- FINISHING: fabrics are finished to make them more useful
There are two types of textile fibres:
NATURAL FIBRES:
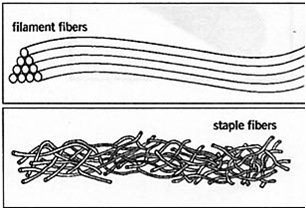
These fibers are found in animals, plants and minerals. They usually have short fibres, called staple fibres. The only exception is silk, which is a continuous long fiber which is 1 kilometres long.
Sources of natural fibres
COTTON from the cotton plant.
- cool to wear
- very absorbent, dries slowly
- soft handle
- good drape
- durable
- creases easily
- can be washed and ironed
Due to the cool to wear and absorbent qualities of Cotton, it is used in everyday wear such as underwear, T-Shirts or undergarments like vests; but they may have a mixture of polyester threads because of the quick-dry qualities.
LINEN from the flax plant.
- fresh and cool to wear
- very absorbent, dries quickly
- stiffer handle
- good drape
- durable
- creases badly
- can be washed and ironed
Linen is used widely in ethical traditional clothing such as the Moroccan Kaftan dress. The fresh and cool to wear, absorbent and quick dry qualities are suitable for garments that are to be worn in or are from hotter countries.
WOOL from sheep.
- warm to wear
- absorbent, dries slowly
- breathable, repels rain
- soft or coarse handle
- can shrink, should be dry cleaned
- good drape
- not durable
- creases drop out
Wool is widely used in colder countries where warmth is needed in outer garments like coats, to prevent the body heat escaping.
SILK from silkworms
- warm to wear
- absorbent
- soft handle
- good lustre and drape
- durable
- creases drop out
- dry clean
China is well known for it’s silk production and the Chinese Qipao (a female dress) is originally made from silk.
SYNTHETIC FIBRES
These are man-made fibres that are made using chemical sources. They are filament fibres which are slender and thread-like meaning it doesn’t always have to be spun into a yarn.
SYNTHETIC FIBRES RESOURCES:
VISCOSE
comes from pine trees or petrochemicals.
- absorbent, dries slowly
- low warmth
- soft handle
- good drape
- not durable
- creases easily
- can be washed and ironed
ACRYLIC, NYLON and POLYESTER come from oil and coal.
ACRYLIC
- warm to wear
- non-absorbent, dries quickly
- stiffer handle, like wool
- good drape
- durable
- crease resistant
- easy care
Due to it’s non-absorbent and quick dry qualities, it is widely used in light sportswear jackets
NYLON
- warm to wear
- absorbent, dries slowly
- breathable, repels water
- soft or coarse handle
- can shrink, should be dry cleaned
- good drape
- durable
- creases drop out
Because it has absorbent and water repelling properties, nylon is likely to be used in coats.
POLYESTER
- low warmth
- non-absorbent, dries quickly
- soft handle
- good drape
- very durable
- crease resistant
- easy care
- can be recycled
Polyester is also used in sportswear just like Acrylic, except it is more durable which is more suitable for scuba suits because it also keeps warmth which will help moderate body temperature whilst underwater.